Thinking about using the sun’s power for your home? Solar power systems are a green and affordable way to cut down on your electricity bills. They also boost your home’s value and help the environment. This guide will cover the basics of solar systems, their parts, and the choices you have.
Key Takeaways
- Solar power systems turn sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic panels, offering a clean energy source for your home.
- A 6 kW solar system can save you about $1,500 a year on your electric bills.
- Installing a solar system takes 2-6 months, including getting permits and passing inspections.
- Solar systems can make your home worth more by about 3.74%, or $14,329 on average.
- Solar panels are very reliable, with most makers promising at least 80% efficiency for 25 years.
Understanding Solar Power Basics
Solar power uses the sun’s energy, a clean source that’s becoming more popular. It works through the photovoltaic effect, where silicon cells turn sunlight into electricity. This energy cuts down your electric bill savings and carbon footprint, appealing to eco-friendly homeowners.
What Makes Solar Energy Work
Solar energy systems use silicon solar cells to make electricity. When sunlight hits these cells, it creates an electrical current. This current powers your home’s devices and gadgets.
The Photovoltaic Effect Explained
The photovoltaic effect powers solar energy. Sunlight’s photons excite silicon electrons, making them move. This movement forms an electrical current, ready to power your home.
Benefits of Solar Energy for Homeowners
- Lower electric bill savings by making your own energy
- Shield against high utility costs and power outages
- Help the environment with renewable energy
- Boost your home’s value with solar power
Solar panels last 25 years or more. Homeowners enjoy long-term renewable energy and electric bill savings.
Solar power is not only environmentally friendly, but it also offers homeowners a chance to take control of their energy costs and contribute to a sustainable future.”
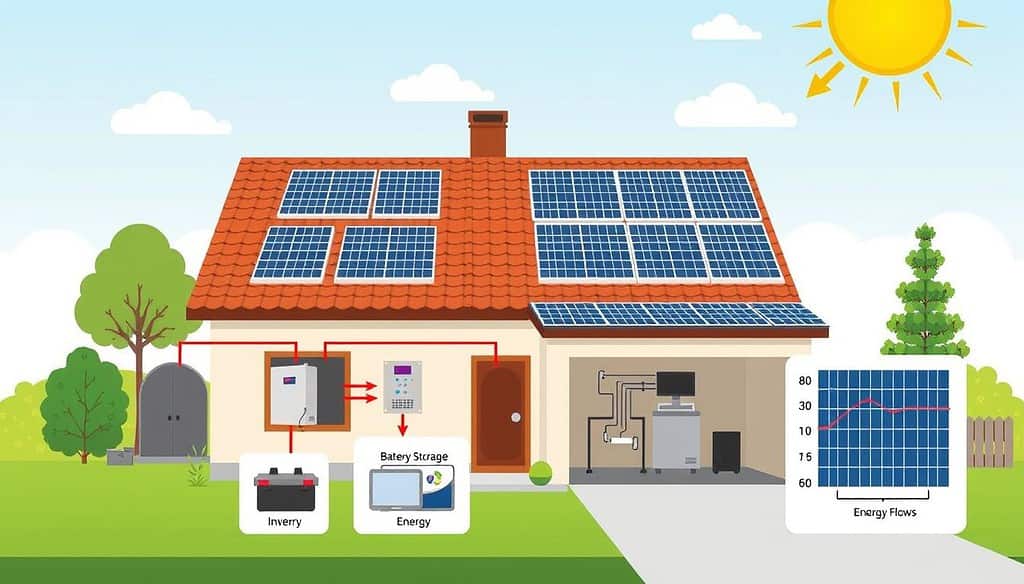
Essential Components of a Home Solar System
Building a home solar system involves several key parts. These parts work together to use the sun’s energy. From solar panels to inverters, each plays a crucial role in powering your home with clean energy.
Solar Panels and Their Function
Solar panels are at the heart of any solar power system. They turn sunlight into electricity. Modern solar panels, like those from LG, can make a lot of power from a small area.
The panel’s efficiency shows how well it turns sunlight into electricity. This is important for getting the most power from your panels.
Inverters and Power Conversion
After solar panels make DC electricity, it needs to be changed into AC. This is where inverters come in. There are string inverters and microinverters for home systems.
These inverters are key for making your solar power work with your home’s electrical system.
Battery Storage Solutions
Battery storage is an optional but popular part of home solar systems. It stores extra electricity for later use. This is great for backup power during outages or when it’s dark.
Batteries make your solar system more reliable and self-sufficient.
Solar panels, inverters, and batteries work together to use the sun’s energy. Understanding each part helps you design a better solar system for your home.
| Component | Description | Typical Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Panels | Photovoltaic devices that convert sunlight into electricity | $2.40 – $5 per watt |
| Inverters | Convert DC electricity from solar panels into AC electricity for home use | Around $0.70 per watt |
| Battery Storage | Energy storage systems that store excess solar energy for later use | Varies based on capacity and technology |

“The majority of customers opt for the simplest possible system on their roofs for the best return on investment.”
Types of Solar Power Systems
There are three main types of solar power systems for homes: grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid. Each has its own features and benefits. Knowing these can help you pick the right solar option for your home.
Grid-Tied Solar Systems
Grid-tied systems are the most common for homes. They connect to the power grid. This lets you use grid power when needed and send extra solar power back to the grid. They’re often cheaper and easier to install than off-grid systems.
Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid systems are standalone and not connected to the grid. They use batteries to store solar energy for later use. They’re great for remote areas without grid access but can be pricier and harder to set up.
Hybrid Solar Systems
Hybrid systems mix grid-tied and off-grid features. They connect to the grid but also have batteries for backup. This makes them a good choice for many homeowners who want both benefits.
| System Type | Grid Connection | Battery Backup | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grid-Tied | Yes | No | Most homes with access to the power grid |
| Off-Grid | No | Yes | Remote locations without grid access |
| Hybrid | Yes | Yes | Homes that want grid-tied benefits with battery backup |
Choosing the right solar system depends on your energy needs, budget, and local rules. It’s key to weigh the pros and cons of each to find the best fit for your home and lifestyle.
Solar Power System For Home: Ultimate Beginners Guide
Planning Your Solar Installation
Starting with solar installation is key to using renewable energy at home. You need to check your energy use, roof condition, and sunlight. This ensures your solar system fits right and works well.
System Sizing and Requirements
The size of your solar system depends on how much energy you use. Usually, a home needs 15-19 solar panels. But, it can change based on your home size, appliances, and daily use. A solar expert can help find the best size for you.
Installation Process Overview
Installing a solar power system takes 2-6 months. This includes designing, getting permits, ordering parts, installing, and checking. Each step is important for safety and following rules. Knowing the process helps you plan your solar project better.
“Solar panels typically last for at least 25 years under warranty, maintaining a minimum of 80% efficiency during this period.”
Understanding Solar Panel Technology
Solar panels are key in using clean, renewable energy for your home. They turn the sun’s energy into electricity for your daily needs. Did you know there are different solar panel types, each with its own benefits?
The main types are monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels. Monocrystalline panels are black and very efficient, with an efficiency of 18-22%. Polycrystalline panels are blue and less efficient, at 15-17%.
What makes solar panels special is the solar cell technology. Solar cells use silicon to turn sunlight into electricity. This is why solar panels are great at making clean energy for your home.
Most home solar panels are 3 feet wide and 6-7 feet tall. This size lets them catch a lot of sunlight. But, the size of your system depends on your energy needs and roof space.
Learning about solar panel technologies helps you choose the right one for your home. With better solar cell efficiency and design, solar energy’s future looks bright.
Solar System Cost and Financial Benefits
Getting a solar power system for your home might seem expensive at first. But, the long-term savings make it a smart choice. Solar panels cost between $2.60 and $3.35 per watt, with a 6 kW system costing about $18,000. But, a 30% federal tax credit can cut down this cost a lot.
After you install solar panels, you’ll start saving money on your electricity bills. Homes with solar panels sell for about 3.74% more than similar homes without them. This means they sell for around $14,329 more. Plus, solar panels are guaranteed to work well for 25 years, and many last even longer.
Long-term Savings Analysis
A solar system can save you about $1,500 a year on electricity. This means you’ll get your money back in about 10 years. With solar panels lasting 25 years or more, you’ll save a lot of money over time. State and local incentives can also help lower the cost, making solar panels even more appealing.
Available Tax Incentives and Rebates
- The federal solar tax credit, also known as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), can reduce the net cost of a solar system by 30%.
- Many states and local governments offer additional incentives, such as rebates, tax exemptions, and performance payments, which can further improve the financial benefits of going solar.
When thinking about getting solar panels, consider a few things. Look at net metering, tax incentives, your electric bill, roof suitability, and how long it’ll take to pay back. With the right mix of costs, incentives, and savings, solar panels can be a great investment for homeowners.
Grid-Tie vs. Off-Grid Solar Solutions
When thinking about solar power for your home, you have two main choices: grid-tie and off-grid systems. Knowing the differences helps you pick the right one for your energy needs and budget.
Grid-Tie Solar Systems
Grid-tie systems connect your home to the power grid. They let you use grid power when needed and send extra solar energy back to the grid. This net metering can lower your electricity bills by giving you credits for the extra energy. These systems are cheaper and easier to set up because they don’t need batteries.
Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid systems work on their own, not needing the grid. They use battery storage to keep power flowing when the sun isn’t out. This ensures your home stays powered up. Off-grid systems give you more control but cost more upfront for batteries and other parts.
Hybrid solar systems are a mix of both. They connect to the grid and have battery backup. This way, you get the benefits of grid connection and a backup power source for outages or high usage times.
| Feature | Grid-Tie Solar | Off-Grid Solar |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Connection | Yes | No |
| Battery Storage | No | Yes |
| Energy Independence | No | Yes |
| Upfront Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Easier | More Complex |
Choosing between grid-tie and off-grid systems depends on your energy needs, budget, and how independent you want to be. Talking to a solar expert can help you decide which system is best for your home and renewable energy goals.

Battery Storage and Energy Management
Homeowners are now looking into solar power more than ever. Battery storage systems play a key role in this. They come in types like lithium-ion and lead-acid, offering many benefits for managing energy.
Battery Types and Technologies
Home solar systems often use lead-acid, gel, and lithium-ion batteries. Lead-acid batteries are cheaper, but lithium-ion ones are more efficient and last longer. Your choice affects how well and how much your solar system costs.
Energy Storage Benefits
Battery storage brings many advantages for solar power users. It lets you live off the grid and have power when the grid goes down. It also helps you use more of the solar energy you make, saving you money on bills.
| Battery Type | Efficiency | Lifespan | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-acid | 80-85% | 5-15 years | $ |
| Lithium-ion | 90-95% | 10-15 years | $$ |
Getting battery storage costs a lot upfront, but it’s worth it in the long run. It helps you save money by using less grid power. This makes it a smart part of your home’s energy plan.

“Battery storage is a game-changer for homeowners with solar power systems, enabling them to maximize the benefits of renewable energy and take control of their energy consumption.”
Solar Panel Placement and Optimization
Putting your solar panels in the right spot is key to getting the most out of them. The best place is a south-facing roof with little to no shade all day. This spot gets the most sunlight, which is vital for making lots of energy.
But, not every home has a perfect south-facing roof. If yours doesn’t, you can still put panels on east or west sides. You might need more panels to get the same energy, though. Make sure your roof is strong and in good shape before you start, as problems can hurt your system’s performance and safety.
Some systems use solar tracking tech. This lets panels move to follow the sun all day. It can boost efficiency by up to 25%, but it makes the system more complex and expensive.
When picking where to put your panels, check the shading on your roof. A little shade can cut down a lot on energy output. So, try to keep trees and buildings away from your panels.
By thinking about roof orientation, tilt angle, and shading analysis, you can make your solar system work better. This means more energy savings and good for the planet too.
| Solar Panel Efficiency | Warranty Period | Property Value Increase |
|---|---|---|
| Over 75% of solar panels outperform their warranty | Solar panels are typically guaranteed to be at least 80% efficient for 25 years | Homes with solar systems see an increase in property value by 3.74% |
“Optimal panel placement is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and energy output of your home solar system.”
Maintenance and Longevity of Solar Systems
Keeping your solar power system in top shape is key to getting the most out of it. Solar panels usually come with a 25-year warranty. But, with the right care, they can keep producing clean energy for even longer.
Regular Maintenance Requirements
Maintaining solar panels is easy. It mainly involves cleaning them a few times a year and checking how they’re doing. Cleaning helps get rid of dirt and leaves that block sunlight and cut down on energy.
Use a soft-bristle brush and water to clean the panels. Make sure to avoid anything too harsh. Also, keep an eye on your system’s performance. Use apps or online tools to track energy output and spot any problems.
System Lifespan and Warranties
Solar panels are built to last, handling the weather and keeping electricity flowing for decades. They’re usually guaranteed to work at 80% of their best for 25 years or more. In fact, over 75% of solar panels do even better than their warranties promise.
While panels last a long time, other parts like inverters need more attention. Inverters turn solar energy into electricity and have warranties from 10 to 20 years. They might need to be replaced once or twice during the system’s life.
By keeping up with maintenance and monitoring, your solar system will run smoothly for years. This will make your investment worthwhile and help the planet.
“Solar panels are typically guaranteed to be at least 80% efficient for 25 years, as per manufacturer warranties.”
| Component | Lifespan | Warranty |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Panels | 25+ years | 25 years |
| Inverters | 10-20 years | 10-20 years |
| Batteries | 5-15 years | 5-10 years |
Common Solar Power Applications
Solar power is versatile and used in many ways. It can power homes and light up outdoor spaces. This makes it a great choice for those wanting to use less traditional electricity and go green.
Residential Solar Power
Residential solar power is big for homeowners. Solar panels on rooftops can power appliances, lights, and gadgets. They also charge electric vehicles and heat swimming pools.
Solar water heating systems are another hit. They’re a green and affordable way to get hot water.
Commercial Solar Power
In the business world, solar power is becoming more popular. Companies use solar panels to cut down on energy costs and carbon emissions. Solar lighting is common too, lighting up parking lots and walkways without the grid.
Solar power is used for more than just electricity and lights. It’s used for water pumping, off-grid systems, and even big solar farms. As tech gets better and prices drop, solar’s uses will keep growing.
| Application | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Solar | Powering homes, charging electric vehicles, heating water | Reduced energy bills, increased property value, eco-friendly |
| Commercial Solar | Powering businesses, providing outdoor lighting, off-grid solutions | Cost savings, sustainable operations, reduced carbon footprint |
| Solar Water Heating | Providing hot water for homes and businesses | Energy efficient, cost-effective, environmentally friendly |
| Solar Lighting | Illuminating outdoor spaces like parking lots and walkways | Reduced energy consumption, low maintenance, eco-conscious |
As solar power grows, so do its uses. It’s becoming a top choice for both homes and businesses looking to use the sun’s power.
“The future belongs to those who believe in the beauty of their dreams.”
– Eleanor Roosevelt
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Homeowners are choosing solar power more and more. This choice is good for the environment. Solar energy cuts down on carbon emissions a lot. A typical home solar system can cut down carbon emissions by up to 4 tons a year.
This helps with sustainable living and environmental conservation. Solar power uses the sun’s energy, which is clean and endless.
Solar panels do have some environmental impact when made. But, this impact is small compared to the benefits. Solar power supports clean energy and helps us use less non-renewable resources. It makes homes more energy independent.
By using solar power, homeowners help create a greener future. They contribute to a world that uses less fossil fuels.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
The U.S. has over 179 gigawatts (GW) of solar power installed. This is enough to power 32.5 million homes. Solar power has grown a lot, helping reduce carbon emissions.
The electric power sector is a big source of greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. Choosing solar power can greatly lower a home’s carbon footprint. It supports a shift to cleaner energy.
Renewable Energy Benefits
Solar energy has many benefits for homeowners. The solar market in the U.S. has grown fast, becoming more affordable. Home solar installations can lower utility bills and support sustainable living.
Big solar farms also make clean electricity for the grid. Solar systems, like water pumps and street lights, help bring renewable energy to more places. They are important in both cities and rural areas.
“The sun, the moon and the stars would have disappeared long ago… had they happened to be within the reach of predatory human hands.”
– Henry Mayers Hyndman
Conclusion
Solar power systems bring many benefits to homeowners. They help cut down on electricity costs and are good for the environment. Plus, they make homes more energy independent.
The cost to start might seem high at first. But, the savings and benefits over time make solar worth it. It’s a smart choice for making your home more sustainable.
As solar tech gets better and prices drop, the future of green energy looks bright. Using the sun’s power can lower your carbon footprint. It also gives you the confidence of being energy self-sufficient.
More people are turning to solar power. This shift is moving us towards a greener energy future. It’s good for both our homes and the planet.
If you want to save on bills, help the planet, or boost your home’s value, solar is a great choice. With proper planning and care, your solar system will keep providing clean energy for years.
Solar power systems for homes turn sunlight into electricity. They help lower your electric bills and increase your home’s value. Plus, they use renewable energy.
Solar energy works by using silicon cells in panels to convert sunlight into electricity. This means lower electric bills and a green energy source. It also helps protect you from rising power costs.
A home solar system has solar panels, inverters, racking, and optional batteries. Panels catch sunlight, inverters change DC to AC power, and batteries store extra energy. You might also need charge controllers, wiring, fuses, and disconnects.
There are three main types: grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid. Grid-tied systems are less expensive and work well for most homes. Off-grid systems are best for remote areas. Hybrid systems offer both grid connection and battery backup.
Planning starts with checking your energy use, roof condition, and sunlight. System sizing depends on how much energy you use. The installation takes 2-6 months, including design, permits, equipment, and final checks.
Solar panels are mostly made of silicon. There are two main types: monocrystalline (black) and polycrystalline (blue). The efficiency of panels is how well they turn sunlight into electricity.
Solar systems cost .60-.35 per watt installed. A 6 kW system costs about ,000 before incentives. With the 30% federal tax credit, costs drop significantly. You can save around
Solar power systems for homes turn sunlight into electricity. They help lower your electric bills and increase your home’s value. Plus, they use renewable energy.
Solar energy works by using silicon cells in panels to convert sunlight into electricity. This means lower electric bills and a green energy source. It also helps protect you from rising power costs.
A home solar system has solar panels, inverters, racking, and optional batteries. Panels catch sunlight, inverters change DC to AC power, and batteries store extra energy. You might also need charge controllers, wiring, fuses, and disconnects.
There are three main types: grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid. Grid-tied systems are less expensive and work well for most homes. Off-grid systems are best for remote areas. Hybrid systems offer both grid connection and battery backup.
Planning starts with checking your energy use, roof condition, and sunlight. System sizing depends on how much energy you use. The installation takes 2-6 months, including design, permits, equipment, and final checks.
Solar panels are mostly made of silicon. There are two main types: monocrystalline (black) and polycrystalline (blue). The efficiency of panels is how well they turn sunlight into electricity.
Solar systems cost $2.60-$3.35 per watt installed. A 6 kW system costs about $18,000 before incentives. With the 30% federal tax credit, costs drop significantly. You can save around $1,500 a year. Systems last 25+ years, with a 10-year payback period.
Grid-tie systems connect to the utility grid, using net metering to lower costs. Off-grid systems need batteries and are pricier but offer energy independence. Hybrid systems combine grid connection with battery backup.
Battery storage options include lead-acid, gel, and lithium-ion. Lithium-ion batteries are the most efficient but cost more. Batteries enable off-grid living, provide backup during outages, and help optimize energy use.
Panels should face south with little shading. They can be installed on other orientations but might need more panels. Roof condition and structural integrity are key. Some systems use solar trackers to follow the sun.
Solar systems need little maintenance, like occasional cleaning and checks. Panels last 25+ years, while inverters may need replacement after 10-20 years. Most manufacturers offer 25-year warranties on panels.
Solar power is used for home and business electricity, water heating, outdoor lighting, and small device charging. At home, it powers appliances, electronics, and lights.
Solar energy cuts down carbon emissions a lot compared to fossil fuels. A typical home system can offset 3-4 tons of carbon annually. While solar panel making has some environmental effects, these are offset in 1-4 years of use.
,500 a year. Systems last 25+ years, with a 10-year payback period.
Grid-tie systems connect to the utility grid, using net metering to lower costs. Off-grid systems need batteries and are pricier but offer energy independence. Hybrid systems combine grid connection with battery backup.
Battery storage options include lead-acid, gel, and lithium-ion. Lithium-ion batteries are the most efficient but cost more. Batteries enable off-grid living, provide backup during outages, and help optimize energy use.
Panels should face south with little shading. They can be installed on other orientations but might need more panels. Roof condition and structural integrity are key. Some systems use solar trackers to follow the sun.
Solar systems need little maintenance, like occasional cleaning and checks. Panels last 25+ years, while inverters may need replacement after 10-20 years. Most manufacturers offer 25-year warranties on panels.
Solar power is used for home and business electricity, water heating, outdoor lighting, and small device charging. At home, it powers appliances, electronics, and lights.
Solar energy cuts down carbon emissions a lot compared to fossil fuels. A typical home system can offset 3-4 tons of carbon annually. While solar panel making has some environmental effects, these are offset in 1-4 years of use.
FAQ
What is a solar power system for homes?
How does solar energy work?
What components make up a home solar system?
What are the main types of solar power systems?
How is a solar installation planned and executed?
What are the different types of solar panels?
What are the costs and financial benefits of a solar system?
What is a solar power system for homes?
How does solar energy work?
What components make up a home solar system?
What are the main types of solar power systems?
How is a solar installation planned and executed?
What are the different types of solar panels?
What are the costs and financial benefits of a solar system?
FAQ
What is a solar power system for homes?
How does solar energy work?
What components make up a home solar system?
What are the main types of solar power systems?
How is a solar installation planned and executed?
What are the different types of solar panels?
What are the costs and financial benefits of a solar system?
FAQ
What is a solar power system for homes?
How does solar energy work?
What components make up a home solar system?
What are the main types of solar power systems?
How is a solar installation planned and executed?
What are the different types of solar panels?
What are the costs and financial benefits of a solar system?
How do grid-tie and off-grid solar systems differ?
What are the battery storage options for solar systems?
How should solar panels be placed and optimized?
What maintenance is required for solar systems?
What are the common applications of solar power?
What are the environmental benefits of solar energy?
How do grid-tie and off-grid solar systems differ?
What are the battery storage options for solar systems?
How should solar panels be placed and optimized?
What maintenance is required for solar systems?
What are the common applications of solar power?
What are the environmental benefits of solar energy?
How do grid-tie and off-grid solar systems differ?
What are the battery storage options for solar systems?
How should solar panels be placed and optimized?
What maintenance is required for solar systems?
What are the common applications of solar power?
What are the environmental benefits of solar energy?
How do grid-tie and off-grid solar systems differ?
What are the battery storage options for solar systems?
How should solar panels be placed and optimized?
What maintenance is required for solar systems?
What are the common applications of solar power?
What are the environmental benefits of solar energy?

