Home solar energy is reshaping how Americans power their homes. Since 2008, over 1 million residential solar energy systems have been installed nationwide. Federal programs like the U.S. Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) have slashed costs by over 70% since 2010, making solar panels affordable for more households. This guide explains how solar works, its benefits, and steps to adopt this renewable energy solution.
Key Takeaways
- Homeowners save up to $500 on solar installations through programs like DAC-SASH, which provides free systems to low-income families.
- Solar systems cut electricity bills by up to 50% and boost home value by $15,000, with panels lasting 25 years.
- Modern solar tech, including Tesla’s Solar Roof tiles, combines efficiency with style, while lithium-ion batteries store excess energy at 89% lower costs than a decade ago.
- Residential solar energy systems convert sunlight into power, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and cutting carbon emissions entirely.
- Government guides like the California Solar Consumer Protection Guide help homeowners navigate installations and financing options like the SCE Solar Marketplace.
Introduction to Home Solar Energy
Home solar energy transforms sunlight into electricity, offering households a sustainable energy alternative. This technology empowers families to reduce reliance on traditional power grids. Solar power for homes uses panels to capture sunlight, turning it into usable energy, and cut utility bills.
What Is Home Solar Energy?
Home solar energy systems convert sunlight using photovoltaic (PV) cells. These panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, which inverters then turn into alternating current (AC) for home appliances. Solar power for homes can power everything from lights to HVAC systems, making clean energy practical for daily life.
The Rising Popularity of Solar Power in American Homes
Over a million U.S. homes now use solar panels. The nation’s solar potential is staggering.
“One hour of peak sunlight holds enough energy to meet the U.S. annual electricity demand.”
With 42 states ranking as “good-to excellent” for solar, more homeowners are adopting this renewable option. State incentives and federal programs have also driven growth, making solar accessible to millions.
How Residential Solar Has Evolved
Solar’s journey spans millennia. Ancient civilizations used sunlight for warmth. Key milestones include:
- 1839: Edmond Becquerel discovers the photovoltaic effect
- 1954: First practical solar cell developed by Bell Labs
- 2020s: Modern panels exceed 25% efficiency with 25-year warranties
Advances in materials and policy shifts—like tax credits—drove costs down. Today’s systems are sleeker and more efficient, making home solar energy a realistic choice for families nationwide.
How Solar Energy Works for Residential Properties
A solar energy system for home turns sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) panels. These panels capture sunlight, converting it into direct current (DC) power. An inverter then changes this into alternating current (AC) electricity your home uses. Excess energy flows back into the grid, and your utility company credits this through net metering.
- Panels: 15–25 panels, each with 60–72 PV cells, generate up to 400 watts per panel.
- Inverters: Convert DC to AC power for home use.
- Meters: Track energy used and sent back to the grid.
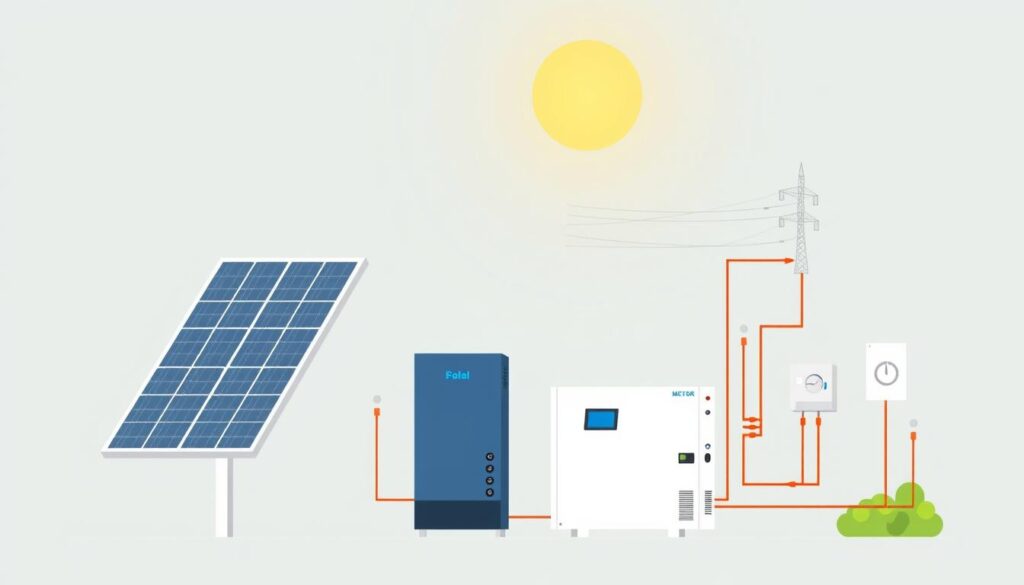
When your system produces more than needed, the grid acts as a storage backup. At night or on cloudy days, your home draws power from the grid. This balance lowers utility bills and reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Renewable energy for homes like this setup can cut annual energy costs by $1,000–$1,500. Over 25 years, savings can reach $20,000–$96,000, with a typical payback period of ten years.
Colorado’s 300+ sunny days annually make it ideal for solar. The state ranks 12th nationally for solar capacity, with systems here often achieving peak efficiency.
Modern systems blend seamlessly with grid power. Inverters can be installed per panel (micro-inverters) or as a central unit, depending on roof layout. The federal tax credit covers 30% of installation costs, lowering upfront expenses. This integration turns sunlight into a reliable, cost-effective energy source for any home.
Benefits of Installing Solar Panels for Your Home
Switching to solar panels for houses delivers tangible rewards for homeowners. From saving money to boosting environmental impact, these systems offer versatile advantages. Let’s break down the top reasons to consider home solar panel installation.
Financial gains lead the list. Installing solar can slash monthly utility bills by up to 30%, with federal tax credits covering 30% of system costs. Over time, savings grow as energy prices rise. Many homeowners recoup their investment within 5–10 years, seeing a 10% average return on investment.
“Solar photovoltaic panels are perceived as upgrades,” noted a study by the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. “Buyers pay up to $15,000 more for homes with solar systems.”
Energy independence is another key perk. Solar-plus-storage systems keep lights on during outages, eliminating reliance on unstable grids. Plus, systems last 25+ years with minimal upkeep—no fuel costs mean steady savings.
- Increased property value through perceived home upgrades
- Monthly bill reductions averaging 20–30%
- Long-term protection against rising utility rates
Environmentally, every home system offsets 3–5 tons of CO2 annually. Choosing solar panels for houses aligns with national clean energy goals, supporting a 30% reduction in U.S. carbon emissions by 2030.
Types of Solar Energy Systems for Residential Use
Choosing the right solar energy solutions for houses starts with understanding the four main options available. Each system addresses different lifestyle and location needs, from urban homes to remote properties.
| Type | Key Features | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Grid-Tied | Net metering, no battery needed | Connected homes with stable grid access |
| Off-Grid | Battery storage, energy independence | Rural/remote properties |
| Hybrid | Battery backup + grid connection | Areas with frequent outages |
| Community | Shared panels, no rooftop needed | Renters or unsuitable roofs |
Grid-Tied Solar Systems
These systems link directly to the utility grid. Excess energy feeds back into the grid, reducing bills through net metering. Ideal for most homeowners, they eliminate up-front battery costs and pay for themselves in 5–10 years. However, they stop working during outages.
Off-Grid Solar Solutions
Off-grid systems require battery banks to store power, making them pricier. Best for areas without grid access, they offer complete independence. Rural landowners often find these cost-effective long-term, as extending utility lines can exceed $20,000 per mile.
Hybrid Solar Energy Systems
Hybrid systems merge grid access with battery backups. During outages, stored energy powers essentials like fridges or HVAC. Popular in storm-prone regions like Texas and California, they combine reliability with energy savings.
Community Solar Options
For those unable to install panels, community solar programs like Southern California Edison’s Green Rate offer clean energy credits. Tenants in multifamily housing can join programs like SOMAH to earn bill credits without owning panels.
The Complete Solar Panel Installation Process
Installing solar panels involves a clear path to energy independence. Let’s break down the home solar panel installation steps so you know what to expect:
- Assessment & Quotes: Start with a free home evaluation. Contractors analyze roof space, energy use, and system needs. Compare quotes from licensed installers to find the best fit.
- Permitting: Secure local permits—this step takes 2–4 weeks on average. Check state rules, like required spacing around panels (often 3 feet).
- Installation: Crews install panels and equipment in 1–3 days. Modern systems prioritize efficiency, with top-tier panels converting 22.8% of sunlight into energy.
- Inspection & Approval: Utility companies review the system. Once approved, a new bi-directional meter is installed to track energy flow.
- Activation: The final step is flipping the switch. Your system starts generating power instantly, slashing electricity bills by up to 100%.

From start to finish, the full residential solar energy setup takes 1–3 months. Most homeowners see their system live in 8–12 weeks. Warranties matter too: panels last 25+ years, while inverters come with 10–12 year guarantees. Need a faster timeline? Prioritize working with licensed installers who streamline permitting. Remember, the home solar panel installation process is backed by the federal tax credit, cutting upfront costs by 30%. Ready to start? Your first step is scheduling that initial consultation—it’s free and takes just 1–2 hours.
Costs and Financial Incentives for Home Solar Power
Investing in home solar energy involves upfront costs, but federal and state programs can significantly reduce expenses. The average solar installation costs around $24,000, but incentives like the federal tax credit cut this by up to 30%. Let’s break down how these savings work.

“The federal solar tax credit can save homeowners up to $7,200 on average,” states the U.S. Department of Energy.
Initial Investment and Pricing Factors
System costs vary by location and system size. A 6kW solar array typically ranges from $15,000 to $25,000. Labor and roof modifications add 10-20% to total costs.
Federal Tax Credits and Incentives
| Year | Tax Credit Rate |
|---|---|
| 2022–2032 | 30% |
| 2033 | 26% |
| 2034 | 22% |
This nonrefundable credit applies to solar panels, batteries, and water heaters. Example: A $20,000 system yields $6,000 in savings through 2032.
State-Specific Solar Rebates
- California’s DAC-SASH program offers up to $24,000 in incentives
- Sacramento residents get $10,000 for battery storage
- Los Angeles provides $480–$1,200 yearly for 20 years
Financing Options for Solar Installations
Options include:
- Solar loans with 3–10 year terms
- Power purchase agreements (PPAs) with no upfront costs
- PACE loans tied to property taxes
California’s PACE loans offer 10–30 year repayment terms with no down payment.
California’s 2024 solar leadership includes rebates like $150/kWh for battery storage. Combine federal credits with state programs to maximize savings—no need to choose between solar power for homes and budgeting wisely.
Energy Savings and ROI of Residential Solar Systems
Understanding the residential solar energy return on investment (ROI) starts with calculating how much you save each year. A typical system costs between $15,000–$50,000, but federal and state incentives like the 30% tax credit cut upfront costs. For example, a $20,000 system drops to $14,000 after the tax break.
- Annual savings average $1,500–$2,880, depending on usage and local rates.
- Pennsylvania homeowners see 8–11-year payback periods, while New Jersey residents may break even in 5 years due to SREC programs.
- A 6kW system can slash utility bills by 70–100%, saving up to $86,400 over 30 years.
“Solar systems boost home equity by an average of 4.1%, per the Lawrence Berkeley National Lab.”
Calculating ROI involves more than just electricity savings. The federal tax credit alone covers 30% of installation costs, and programs like California’s SASH provide extra rebates. A $20,000 system with 25-year savings could yield a 10% annual return—better than many traditional investments. Even after a 10-year payback period, panels generate free energy for decades, shielding households from rising utility prices.
Systems like the EcoFlow 10kWh kit (starting at $9,999) offer tailored solutions. Pairing them with solar panels reduces monthly bills to as little as $10, while state incentives like Arizona’s 25% tax credit lower initial costs further. Over 25 years, these choices deliver total savings exceeding $40,000—making renewable energy for homes a long-term financial win.
Environmental Impact of Home Solar Solutions
Home solar energy transforms everyday living into a force for environmental good. These systems slash pollution and curb climate threats, offering tangible benefits for communities and ecosystems.
A typical residential solar setup cuts 3–4 tons of CO2 yearly—equivalent to removing two gas-powered cars from roads annually. Here’s how it works:
Reducing Your Carbon Footprint
- Average annual CO2 reduction: 3–4 tons
- Eliminates sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter
- 30-year lifespan equals 100+ tons of CO2 avoided
Decreasing Dependence on Fossil Fuels
| Energy Source | Water Use | CO2 Emissions |
|---|---|---|
| Fossil Fuels | High water withdrawal | Heavy CO2 output |
| Home Solar | No water needed | Zero operational emissions |
Solar’s Role in Combating Climate Change
Every rooftop system joins global efforts to replace coal and natural gas. Over three decades, a single home solar array prevents more than 100 tons of CO2—supporting a cleaner energy grid and slowing global warming trends. These choices multiply when communities adopt solar energy solutions for houses, creating ripple effects across regions.
By choosing solar, households cut pollution and inspire broader shifts toward renewable energy systems. The shift from coal to home solar energy also reduces acid rain precursors and smog-forming chemicals, improving air quality nationwide.
Maintenance Requirements for Solar Panels
Solar panels for houses are built to last, requiring minimal upkeep. Most systems need only basic care to keep producing energy efficiently for decades. Here’s what homeowners should know.
- Clean panels 2–4 times yearly to remove dust, debris, or bird droppings.
- Inspect wiring and mounts every 3–5 years through professional home solar panel installation technicians.
- Use monitoring apps to track energy output and spot performance drops.
Weather plays a role too. Light rain naturally cleans tilted panels, while heavy snow may need gentle sweeping. Strong winds or storms? Check for cracks or loose parts after severe weather. Tree branches near panels should be trimmed yearly to avoid shading or debris buildup.
“Solar panels are designed to withstand hail and hurricanes, but annual checks ensure long-term reliability.”
Most manufacturers offer 25-year warranties covering defects and performance. To keep warranties valid, follow maintenance schedules. Professional inspections cost $150–$300, while DIY cleaning saves money. Avoid harsh chemicals—soft brushes and mild soap work best.
Over time, energy output may dip slightly (about 0.5% yearly), but modern panels retain 80–90% of their original capacity even after 25 years. Prioritizing routine care keeps your investment running smoothly and safely.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Home Solar Energy
Adopting solar energy solutions for houses brings many benefits, but challenges like weather, roof conditions, and system choices can arise. Here’s how to address them:
Weather and Climate Considerations
Cloudy regions may reduce output, but modern solar panels for houses still work efficiently. Use tracking systems or high-efficiency panels to maximize production even in moderate sunlight. For example, bifacial panels capture reflected light, boosting yield by 10-15% in varied climates.
Roof Suitability and Structural Issues
Old roofs or shaded areas might hinder installations. Ground-mounted systems or community solar programs offer alternatives. Check roof age and structure before installing—repairs may be needed to support panel weight.
Energy Storage Solutions
| Type | Efficiency | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion Batteries | 80-90% | $8,500–$10,000 |
| Lead-Acid Batteries | 70-80% | $5,000–$7,000 |
Batteries like Tesla Powerwall or Enphase IQ pair well with solar systems. Use this table to compare options and choose based on budget and energy needs.
Finding Qualified Solar Installers
Search the SCE Solar Marketplace or California DG Stats to find licensed contractors. Look for NABCEP-certified technicians and read reviews. Always request multiple quotes to ensure fair pricing.
Conclusion: Embracing a Solar-Powered Future
Renewable energy for homes is reshaping how Americans approach electricity. Solar power for homes offers a clear path to savings, with most homeowners cutting energy bills by 50-75%. A $20,000 solar system can qualify for federal tax credits saving over $5,200, making the upfront costs more manageable. Beyond finances, solar systems add lasting value—properties with panels sell 20% faster and gain up to 4.1% in resale value. This boost translates to thousands of dollars in equity for a $500,000 home.
Emerging innovations like smart inverters and advanced battery storage are making solar systems even smarter. Companies like Tesla and SunPower are developing integrated solutions that pair energy generation with storage, ensuring reliability even during cloudy days or outages. As panel efficiency improves, even homes with smaller roofs can benefit from modern technology.
Switching to solar isn’t just about saving money—it’s a step toward cleaner air. Widespread adoption prevents billions in health costs linked to pollution. With panels lasting 25-30 years, this choice offers long-term stability. Start by comparing local incentives like California’s Solar Initiative or New York’s NY-Sun Program. Contact certified installers to assess your roof’s potential. Every home that chooses solar helps build a greener energy future—one that’s both practical and powerful.
FAQ
What is a home solar energy system?
How do solar panels work?
What are the financial benefits of installing solar panels?
Are there any incentives for installing solar energy systems?
What are the different types of solar energy systems available for homes?
How long does the solar panel installation process take?
What maintenance do solar panels require?
How does solar energy impact the environment?
What challenges might I face when installing solar panels?
Can solar panels work in cloudy or rainy climates?

